在本研究中,我们基于高电活性微生物硫还原芽孢杆菌(G. sulfurreducens)开发了一种用于降解乙酸的微燃料电池驱动型PMS活化系统。该系统采用石墨板作为电极,阳极接种成功形成以硫还原芽孢杆菌为主导的高电活性生物膜,阴极腔室则注入含乙酸的合成废水。通过系统评估关键操作参数(包括初始pH值、PMS用量、ACV浓度及共存阴离子的影响),全面研究了该MFC/PMS混合系统的ACV去除效率。通过代谢组测序与转录组分析,解析了微生物群落结构,并鉴定出编码阳极直接胞外电子传递相关蛋白的关键基因。利用液相色谱-质谱联用技术(LC-MS)识别中间产物,阐明了降解机制并提出潜在降解途径。此外,通过综合分析与生物测定方法,预测了降解过程中矿化效率与生物毒性演变的动态变化。综上,该生物电化学-高级氧化工艺(AOP)混合技术不仅为高效去除阿司匹林等难降解药物提供了新策略,更对开发可持续、能量中性的水处理范式具有重要启示意义。
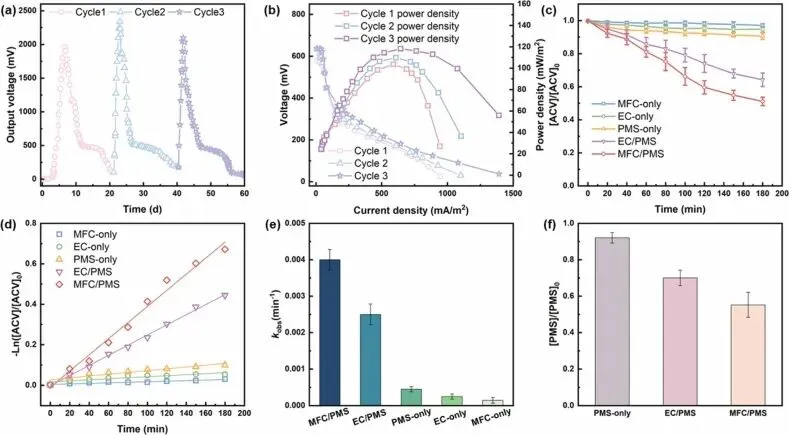
Fig. 1. Degradation of ACV and MFC performance by different catalytic systems. (a) Output voltage of MFC. (b) power density and polarisation curves of MFC during stable operation. (c) Degradation rate of ACV. (d) Kinetic Fit Curve. (e) k value. (f) PMS consumption rate.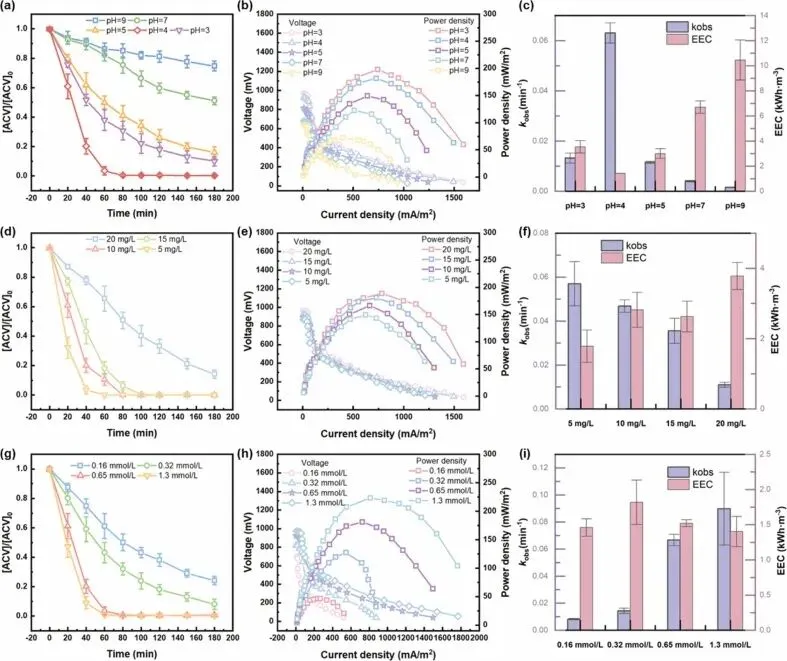
Fig. 2. Effectiveness of MFC/PMS systems in degrading ACV under different operating conditions. (a) ACV degradation efficiency, (b) power density/polarization curves, and (c) k value with EEC under varying pH conditions. (d) ACV degradation efficiency, (e) power density/polarization curves, and (f) k value with EEC under varying initial ACV concentrations. (g) ACV degradation efficiency, (h) power density/polarization curves, and (i) k value with EEC under varying PMS dosages.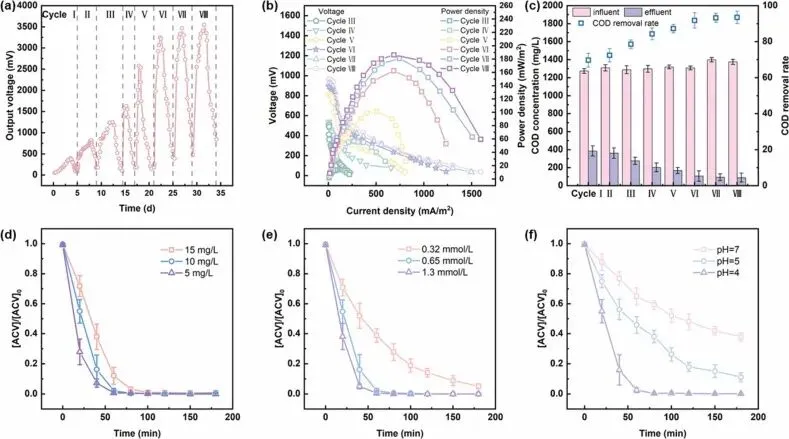
Fig. 3. Performance of the mixed-culture MFC/PMS system. (a) Output voltage across cycles during reactor startup. (b) Power density and polarization curves during system activation. (c) COD variation in anolyte during MFC operation. (d) ACV degradation efficiency under varying initial concentrations, (e) PMS dosages, and (f) pH conditions.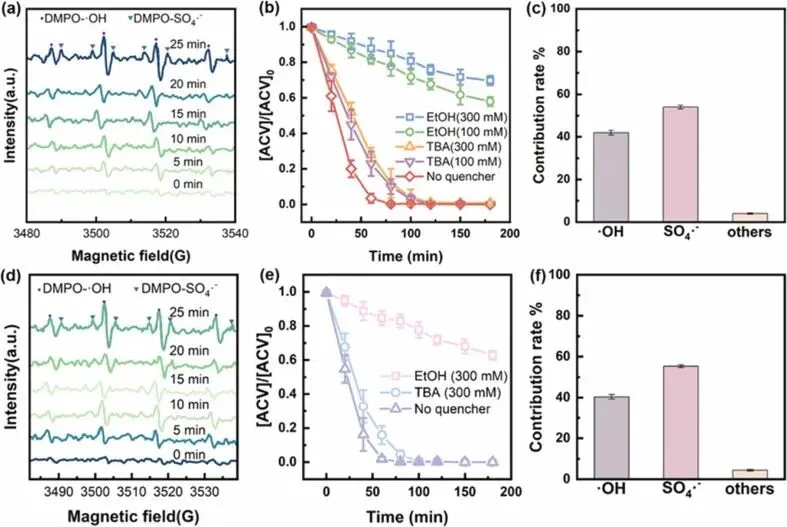
Fig. 4. Pure-culture MFC/PMS system (a) EPR spectra, (b) ACV degradation efficiency with quenchers, (c) Radical contribution percentages. Mixed-culture MFC/PMS system (d) EPR spectra, (e) ACV degradation efficiency with quenchers, (f) Radical contribution percentages.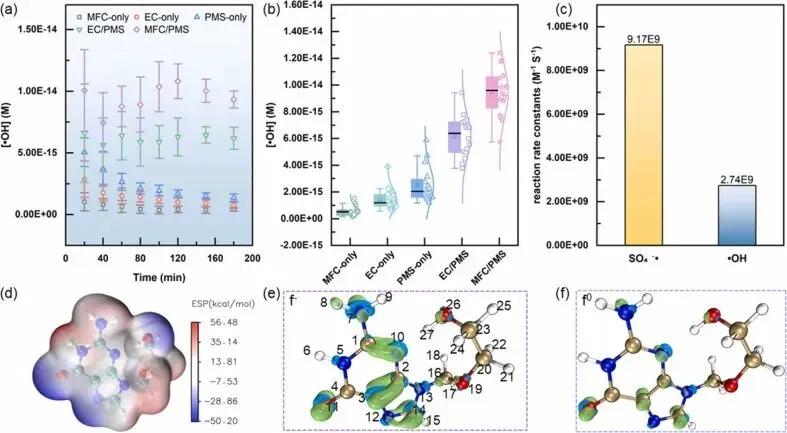
Fig. 5. (a) Time-varying hydroxyl radical concentration, (b) Statistics of hydroxyl radical concentration in different reaction systems, (c) Reaction rate constants for the reaction of SO4•- and •OH with ACV[71], (d) Surface electrostatic potential of ACV, (e) Isosurfaces of the Fukui (-) (Data are presented in Supplementary Table S6 and Table S7), (f) Isosurfaces of the Fukui (0) (Data are presented in Supplementary Table S6 and Table S7).综上所述,通过利用微生物燃料电池激活活性炭(PMS)降解丙酸(ACV),构建了一套经济高效且节能的系统,展现出显著的应用潜力。该微生物燃料电池/活性炭系统表现出卓越的性能与稳定性,在pH值4、活性炭剂量0.65–1.3 mmol/L、初始丙酸浓度5–15 mg/L的条件下,实现了近100%的丙酸去除率。PMS的电化学活化主要归因于MFC产生的周期性电流。通过EPR谱分析、淬灭实验及无机离子效应分析,证实了SO₄•⁻与•OH的共存,其中SO₄•⁻起主导作用。在MFC启动过程中,输出电压稳步上升,伴随发电量显著提升,最大功率密度达187.1 mW/m²。阳极生物膜中Geobacter相对丰度激增至27.4%,编码胞外电子传递相关蛋白的基因(pilA、omcB、omcZ、omcS、omcT、omcE)表达上调。这些结果凸显了MFC/PMS系统卓越的PMS活化与ACV降解效能,不仅彰显其实际应用价值,更为推进电化学反应器在有机污染物降解领域的应用提供了关键性启示。
Haoyong Li, Zhao Liang, Yinhui Huang, Chuanqi Liu, He Dong, Jinru Zou, Pengsong Li, Dezhi Sun, Yongze Liu, Yan Dang, High-efficiency and low-energy degradation of acyclovir through peroxymonosulfate activation by microbial fuel cells, Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2026, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2025.125808
声明:本公众号仅分享前沿学术成果,无商业用途。如涉及侵权,请立刻联系公众号后台或发送邮件,我们将及时修改或删除!
邮箱:Environ2022@163.com