青岛农业大学于艳教授等:基于有限元分析的丘陵山区自走式花生播种机行走底盘机架轻量化设计
- 2026-02-14 16:43:38
于艳,伊大志,王家胜*,谭晓志,王晓敏,董伟康,宋宇帅
(青岛农业大学机电工程学院,青岛266109,山东,中国)
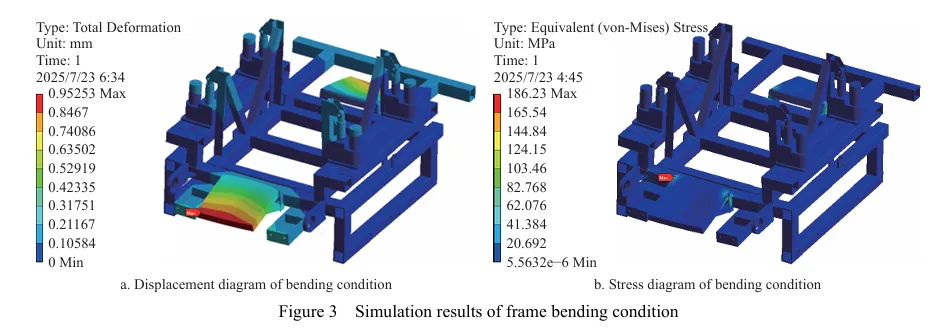
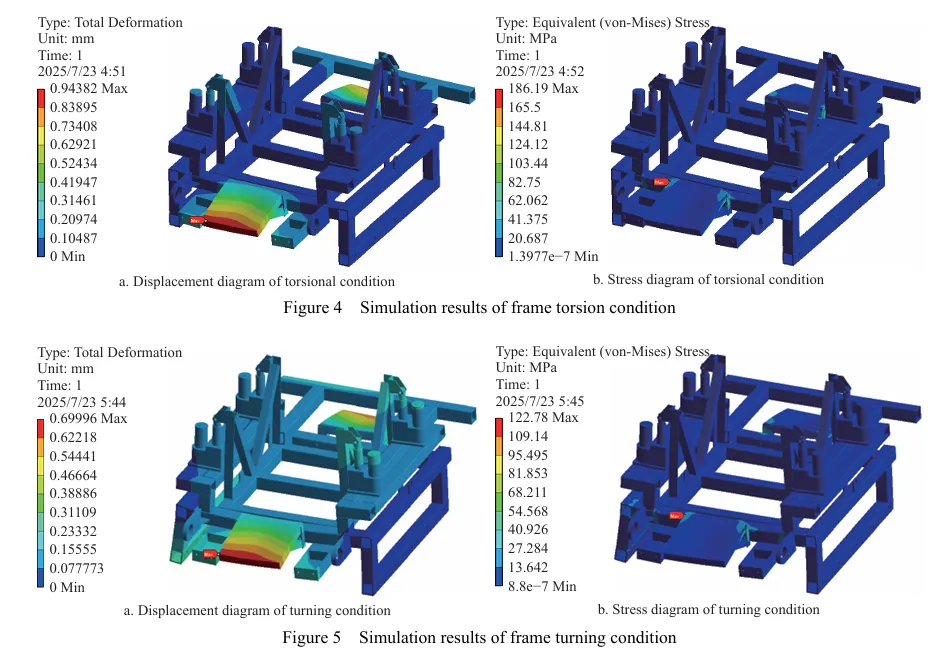
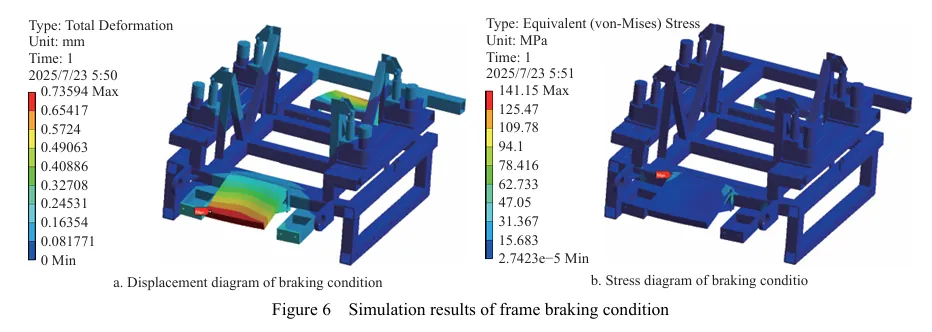
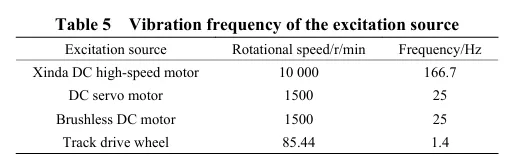
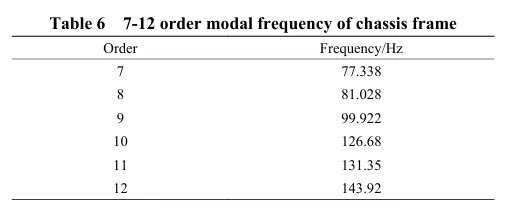
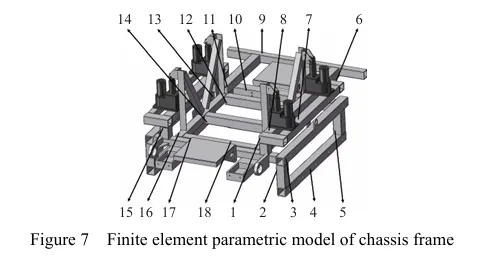
摘要:丘陵山区自走式花生播种机行走底盘机架是整机的主体支撑结构,其重量直接影响播种机的作业性能。因此针对丘陵山区自走式花生播种机结构偏重、强度冗余、续航短的现象,为了减轻整机质量、节约资源、增加播种机续航时间,该研究以自走式花生播种机的行走底盘机架为研究对象,基于Solidworks对行走底盘机架进行三维建模,通过ANSYS Workbench建立行走底盘机架的有限元模型,对其进行模态分析和4种不同工况下的静力学分析。
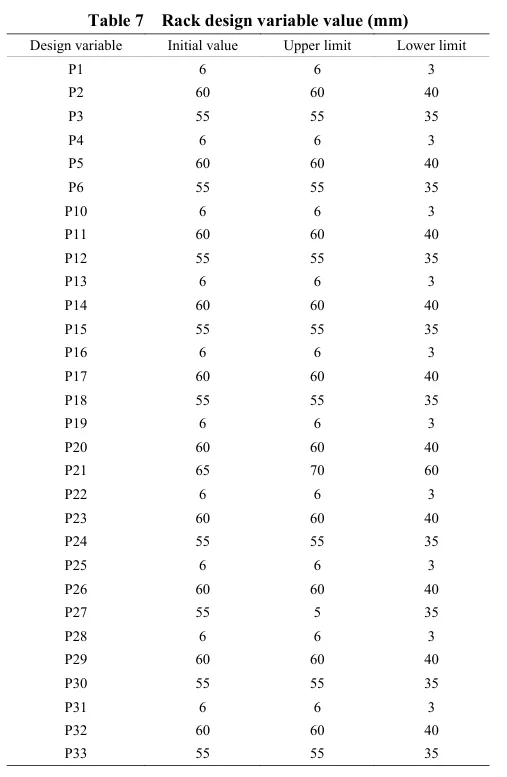
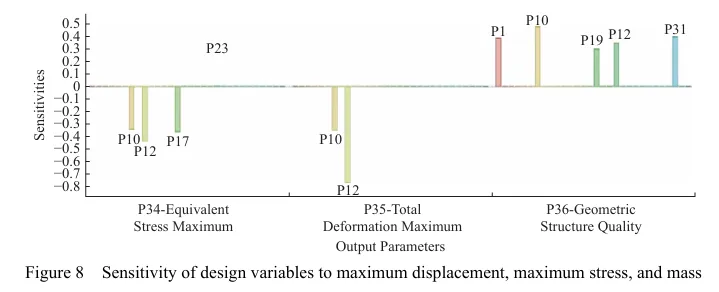
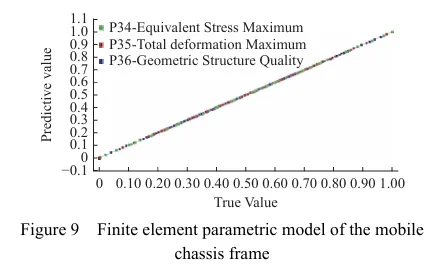
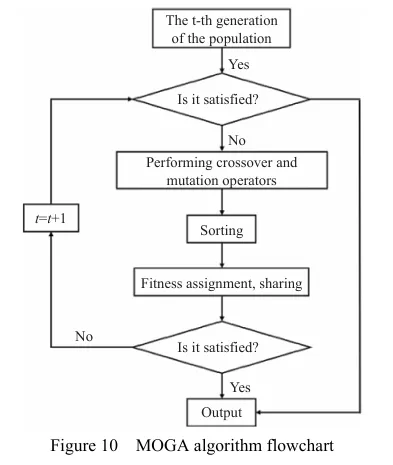
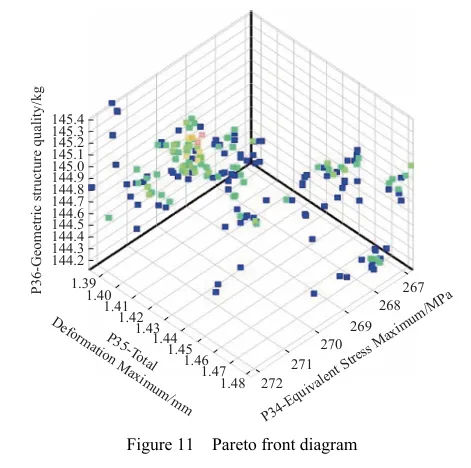
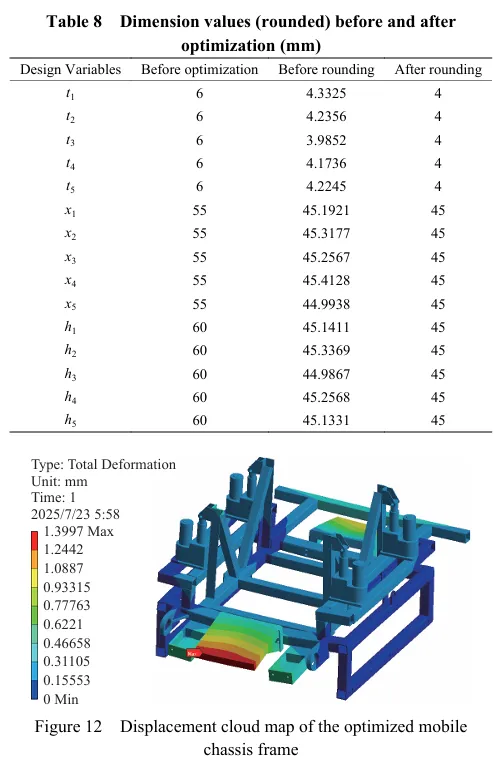
基于灵敏度分析,筛选出行走底盘机架的设计变量,结合拉丁超立方设计方法以及Kriging近似模型模拟得出设计变量之间的响应关系。最后基于MOGA算法进行多目标轻量化设计。结果表明:优化后行走底盘机架质量减轻28.9%,且满足强度要求。田间试验表明:株距合格率均≥98%;播深作业性能稳定,平均播深合格率≥90%,轻量化设计后样机结构稳定,性能可靠。研究结果可为丘陵山区自走式花生播种机行走底盘机架的结构优化与设计提供参考和理论依据。
关键词:自走式花生播种机;行走底盘机架;多目标优化;轻量化设计;有限元分析
DOI: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20251805.9447
引用信息: Yu Y, Yi D Z, Wang J S, Tan X Z, Wang X M, Dong W K, et al. Lightweight design of the chassis framework for a self-propelled peanut planter in hilly areas based on finite element analysis. Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2025; 18(5): 117–126.
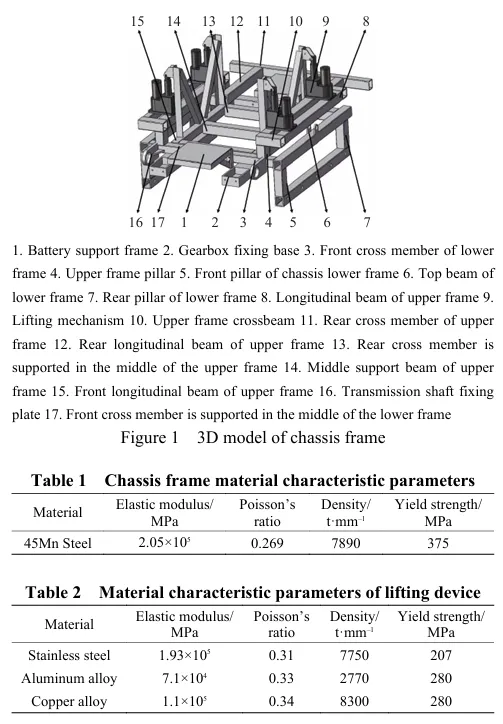
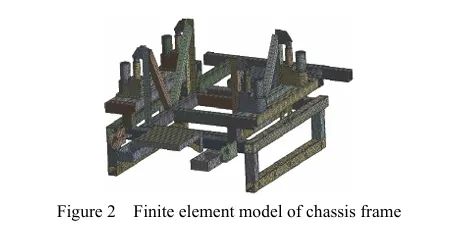
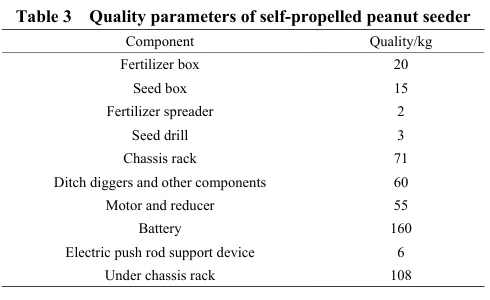
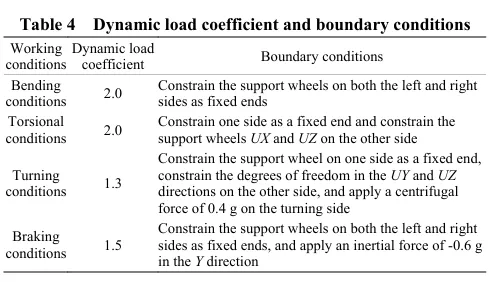

Lightweight design of the chassis framework for a self-propelled peanut planter in hilly areas based on finite element analysis
Yan Yu, Dazhi Yi, Jiasheng Wang*, Xiaozhi Tan, Xiaomin Wang, Weikang Dong, Yushuai Song
(College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Qingdao Agricultural University, Qingdao 266109, Shandong, China)
Abstract: The chassis frame of the self-propelled peanut seeder in hilly and mountainous areas is the main supporting structure of the entire machine, and its weight directly affects the operational performance of the seeder. Therefore, in response to the issues of structural heaviness, strength redundancy, and short endurance of the self-propelled peanut seeder in hilly and mountainous areas, this study aims to reduce the overall weight of the machine, conserve resources, and extend the seeder’s endurance time. The research focuses on the chassis frame of the self-propelled peanut seeder, utilizing SolidWorks for 3D modeling. A finite element model of the chassis frame is established using ANSYS Workbench, followed by modal analysis and static analysis under four different working conditions. Based on sensitivity analysis, design variables for the chassis frame are selected, and the response relationships between these design variables are simulated using the Latin Hypercube Design method combined with the Kriging approximation model. Finally, a multi-objective lightweight design is conducted based on the MOGA algorithm. The results indicate that the optimized chassis frame mass is reduced by 28.9%, while meeting the strength requirements. Field tests indicate that the plant spacing qualification rate is ≥98%; the seeding depth operational performance is stable, with an average qualification rate of seeding depth ≥90%. After lightweight design, the prototype structure is stable and the performance is reliable. The research results can provide reference and theoretical basis for the structural optimization and design of the walking chassis frame of self-propelled peanut planters in hilly and mountainous areas.
Keywords: self-propelled peanut planter, chassis framework of the walking platform, multi-objective optimization, lightweight design, finite element analysis
DOI: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20251805.9447
Citation:Yu Y, Yi D Z, Wang J S, Tan X Z, Wang X M, Dong W K, et al. Lightweight design of the chassis framework for a self-propelled peanut planter in hilly areas based on finite element analysis. Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2025; 18(5): 117–126.
END

点赞
收藏
分享
